Anti-Inflammatories: To Take Or Not To Take?! (Get out of pain now!)
Nov 22, 2022
It's fairly common practice, honestly, to pop some Ibuprofen for aches and pain, whether it be a headache or a muscle spasm or an injury. Hell, I grew up being tossed a few 200mg pills if something started naggin me during soccer or whenever. But is that really the answer? Is there an action that would be better that would still get you the desired result of dampening the pain?!
The answer is not only yes, but an emphatic YES!
And that, my friend, is movement and maybe some manual work. But let's unpack that a bit because (1) it's not just any movement and (2) I bet you have a lot of questions about why.
Let's start with why NSAIDs (non steroidal anti inflammatories - the category that Ibuprofen, Asprin, Aleve, Voltaren, and the likes fall under) are NOT the answer:
Quick side note: Did you know that there are over 90 million presciptions for NSAIDs filled in the US every year?! And that's not even getting into the over-the-counter options that account for several extra millions of dollars in sales. Despite how common they are, there are several risks that might be bigger than you think...
- One of the biggest (and most well known) risks is gastrointestinal (GI) issues. Specifically, GI ulcers or hemorrhage. In fact, if you're taking NSAIDs, your chance of a gastric ulcer is 10-20% (up to 10x higher risk than if you're not taking NSAIDs). Ulcers can lead to hemorrhage or perforation, which can be fatal. (Couldn't find the risk/rate of that occuring, but it does seem like in cases that were fatal, up to 80% were in people on NSAIDs) (ref: Savaas et al 1991, Babb et al 1992)
- Another risk is cardiovascular issues and even stroke. Most NSAIDs can increase your risk of stroke. To note, a study by Garcia-Posa et al did not find a link to stroke with naproxen or ibuprofen (though they did with others). Barthelemy et all in 2011 did find that long term (2 year) use of all NSAIDs, including naproxen and ibuprofen, increased your risk of stroke by 64%
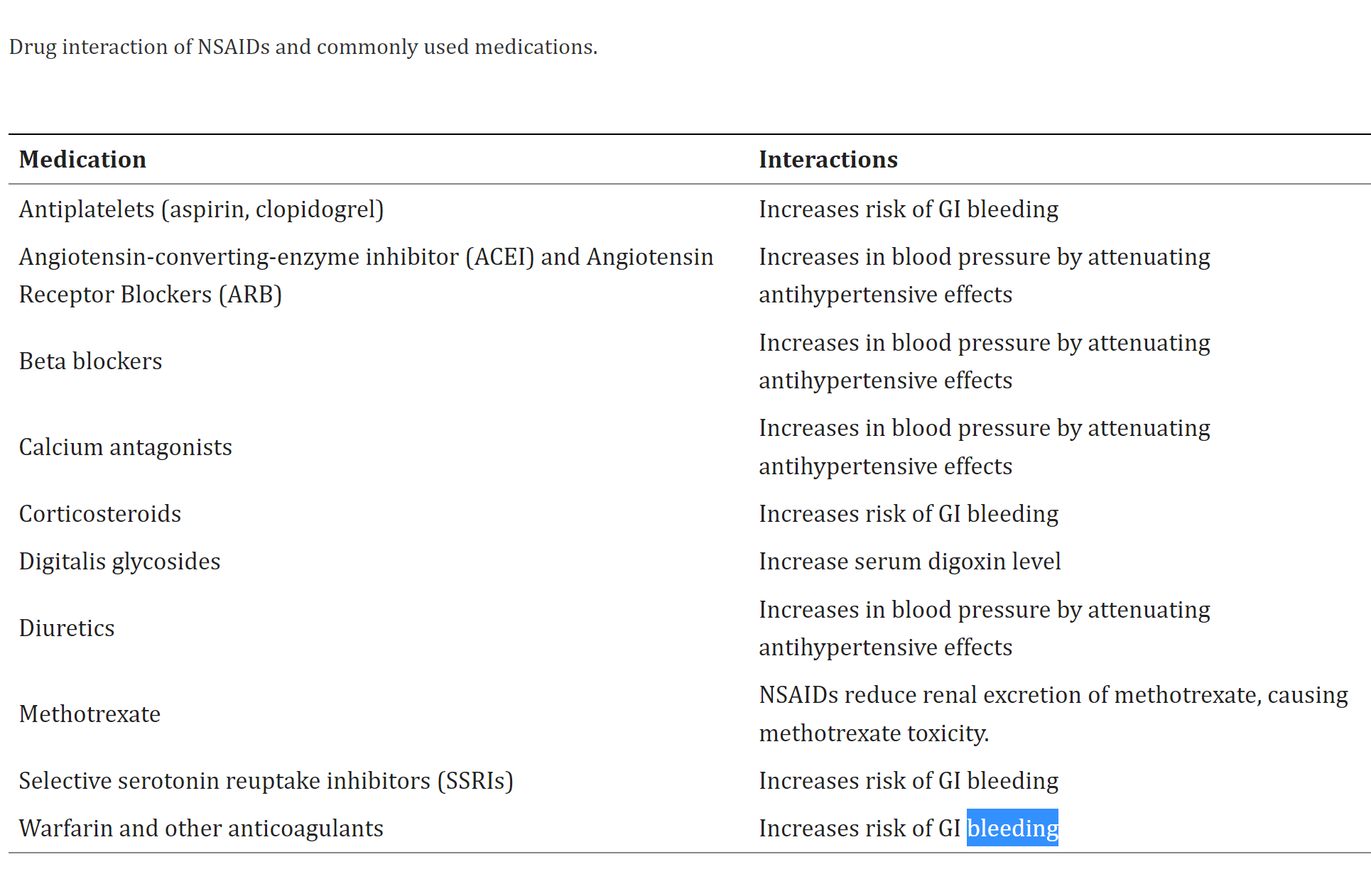
- There are a ton of negative drug interactions to be considered with taking NSAIDs that, unless you're getting prescription strength ones where MAYBE a pharmacist might realize it's connection with other drugs you're on and warn you, you may not be aware of. (Chart below from Wongrakpanich et al, 2018, A Comprehensice Review of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug...)
Ok, the LAST thing that I want this information to do is intill a ton of fear around anything. I simply want you to think twice about why you're popping pills to take the edge off. I myself have taken prescription strength Ibuprofen after each of my knee surgeries because, well at the time I didn't know the options that I'm about to get into and 800mg of Ibuprofen was far better than popping Oxy or Loratab at age 11 (or 15 or 19 - my other 2 surgeries). There are times where it's the "better evil" and warranted. But for the vast majority of the time when it's a relatively minor ache/pain (ankle sprain, tweaked back/neck, pulled shoulder, etc), think about trying movement and muscle activation first! Seriously. Let's dive into it:
Probably not a shocker if you've been following me for awhile that I'm gonna have a "movement is medicine" approach here!

Did you know that isometrics (where a muscle acts against a non moving object, causing a static activation) can be analgesic, especially for tendon issues?! Which is the exact outcome that someone is poppin ibuprofen for. Except isometrics don't come with any of those nasty side effects. Win-win. Ok, so how do you do them in a way that causes that desired decrease in pain?
You perform 5 sets, each time holding 45" and then resting 2 min (or doing exercises for unrelated musculature during that time).
How do you chose the exercise?
Well, the effect is going to be local to what's active during the isometric, so you wanna do something that isolates out the muscle/tendon that's painful. Sounds counterintuitive, I know, to work the tissue that's in pain in order to decrease pain. But when it's done in this way, it really works! Think of what movement that muscle does, and then you wanna perform an isometric of that movement at a partial range point. Here are some examples:
- Bicep tendonopathy: isometric bicep "curls" at 90 deg performed against the bottom of a table
- Patellar tendonopathy: knee extension isometrics performed at about 45 deg flexion (can be into a bench or using a knee extension machine set there with enough weight that you can't actually move it)
- Adductor tendonopathy (often shows up as groin pain. Possibly medial knee pain): Copenhagen planks (Note that the full leg itteration is tough and may be too much just yet...stabilize above the knee to start and progress accordingly)
Ok, hopefully that gives you some ideas for the isometric! And then here's my favorite thing to do for the 2 min rest as well as for literally any pain: Cardio. Get the blood pumping in order to get a full body fluid flush, aka flush out the inflammatory chemicals piling up in the area causing pain. Now, the trick here is to not involve the painful area. Pain in your leg? Hit the arms-only bike. Shoulder pain? Hit the bike using only your legs. Back pain? Arms-only bike and then standing or sitting will depend on what feels best (during and after). And I don't mean just piddling around on the bike. If you put it with isometrics, it'll look something like this:
15' EMOM (every minute on the minute - ie minute 1 you do the 1st, min 2 the 2nd, and then keep rotating through for 15 min to get 5 rounds):
- 30" bike sprint (80% effort if you're on an Echo or Assault bike. You can also crank the resistence up on something like a Peleton to get the effect here. Otherwise, make this a 45" all-out effort)
- 45" isometric
- Rest
You should be breathing pretty heavy getting off the bike and wanting that rest in the 3rd minute! You will also be amazed at how much better you feel after doing this! Legit every person I've worked with and had do this has noticed significat pain reductions. And the best part? They now have a formula for something to try first if anything pops up down the road! #autonomy WIll this solve every issue? Absolutely not. But it will help calm pain down enough to be able to get to the work (aka loading) that those tissues need to really recover and become more resilient.
Outside of acute tendon issues, the cardio/blood flow is still a go-to to dampen pain for just about everything. Even headaches! But that's something we can really dive into another time...
Give it a shot and let me know what you think! Please comment or DM me with any questions about this. And of course, if you have something going on that you'd like a little more in depth personalized help with, jump on a call with me or book a session!
Because I have to put this. This is not individualized medical advice or diagnostic information. This is purely educational.
SUBSCRIBE FOR WEEKLY LIFE LESSONS
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, metus at rhoncus dapibus, habitasse vitae cubilia odio sed.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.

